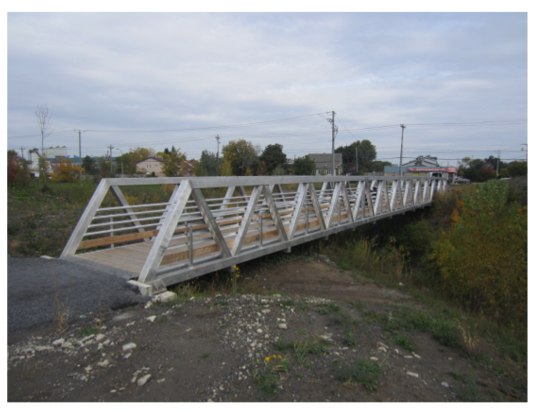
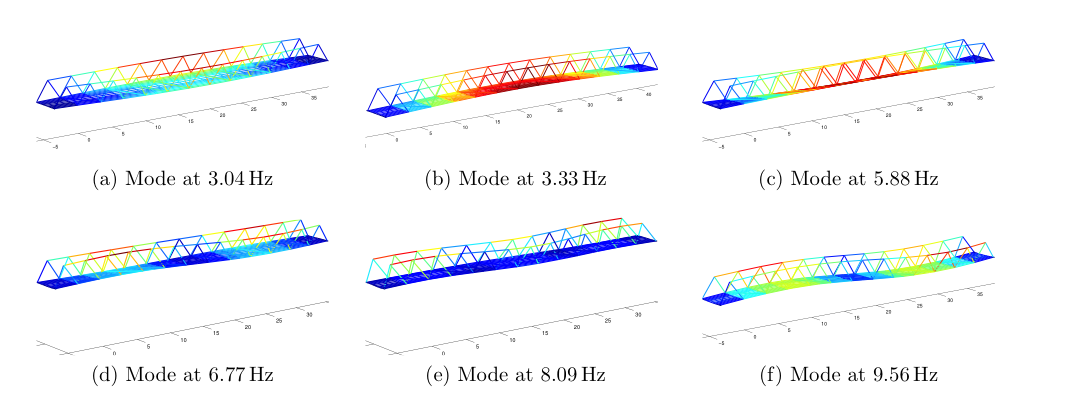
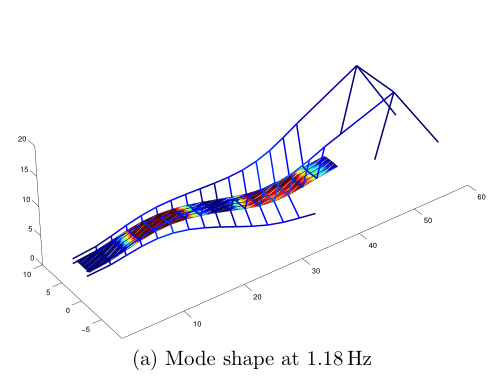
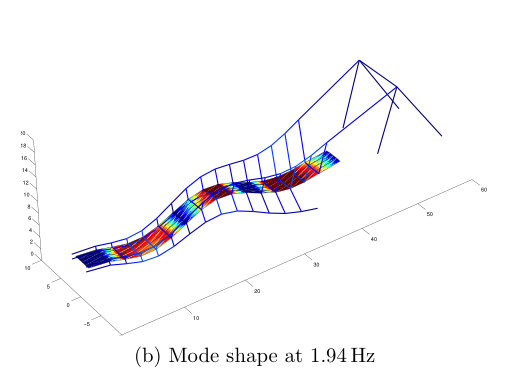
Modal analysis is the process of extracting the modal properties (i.e. natural frequencies, modeshapes and damping ratios) from vibration measurements. Traditional methods have utilized controlled inputs (white noise, impact) to estimate these properties. Research in our group has focused on output-only measurements to extract modal properties. Such methods are extremely useful for large structures as controlled inputs are often impractical to impose. However, lack of control of the provided inputs poses unique mathematical difficulties in the process of modal estimation. Simply put, if we imagine a system of linear algebraic equations, y=Ax, where y are the measurements and x the inputs, then infinite combinations of A (think of this as being the system parameters containing the unknowns) and x result in the same y. Therfore, extracting A is not possible without at least imposing probabilistic assumptions regarding the nature of the inputs. We have addressed these problems within the context of blind source seperation (BSS). Work in our group has resulted in powerful hybrid techniques where traditional BSS methods have been hybridized with time-frequency analysis to yield solutions for cases of closely-spaced modes, underdetermined mixtures and decentralized measurements.